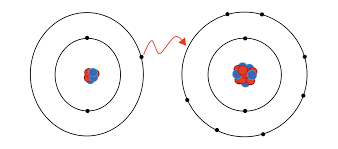
Entende-se por ligação química a união entre átomos. Contudo, será que todos os átomos são capazes de se ligar a outros?
Para que uma ligação química ocorra, são necessárias certas condições, e elas podem ser divididas em 3 tipos: Covalente, iônica e metálica.
Todas essas ligações têm uma regra em comum, a chamada regra do octeto, onde a meta da ligação é adquirir uma estabilidade, 8 elétrons na sua última camada, ou também chamada, camada de valência.
Ligação Covalente
De modo bem simplificado, poderíamos dizer que a ligação covalente acontece entre átomos que têm tendência a ganhar elétrons. Porém, como não é possível que todos ganhem, cada átomo ‘‘empresta’’ um, dois, três ou até quatro elétrons, isto é chamado de compartilhamento de pares eletrônicos. Essa ligação ocorre entre elementos ametais.
Ligação Iônica
Como o nome sugere, as ligações iônicas se formam pela atração de íons de cargas opostas. As ligações iônicas somente ocorrem entre ametais e metais. O cátion é um átomo de metal e o ânion é um não metal.
Cátion: Átomos que perdem elétrons( ficam carregados positivamente).
Ânion: Átomos que ganham elétron (ficam carregados negativamente).
Ligação Metálica
A ligação metálica acontece entre átomos de metal que possuem tendência a perder elétrons e, ao se unirem, formam um retículo. A ligação se faz pelo aparecimento de uma “nuvem de elétrons livres”, a qual envolve os átomos e não pertence a nenhum deles em especial. Para os cientistas, a presença dessa nuvem explica a boa condutividade que os metais apresentam em relação à eletricidade, maleabilidade e a ductilidade.
Chemical bonds
Chemical bonding means the union between atoms. However, are all atoms capable of bonding to others?
For a chemical bond to occur, certain conditions are necessary, and they can be divided into 3 types: covalent, ionic and metallic.
All of these bonds have a common rule, called the octet rule, where the goal of the bond is to acquire stability, 8 electrons in its last shell, or also called the valence shell.
Covalent bond
In a very simplified way, we could say that the covalent bond happens between atoms that tend to gain electrons. However, as it is not possible for everyone to win, each atom “borrows” one, two, three or even four electrons, this is called sharing electron pairs. This connection occurs between ametals elements.
Ionic Bonding
As the name suggests, ionic bonds are formed by the attraction of ions of opposite charges. Ionic bonds only occur between metals. The cation is a metal atom and the anion is a non-metal.
Cation: Atoms that lose electrons (become positively charged).
Anion: Atoms that gain electrons (are negatively charged).
Metallic Bonding
The metallic bond occurs between metal atoms that have a tendency to lose electrons and, when they come together, form a lattice. The connection is made by the appearance of a “cloud of free electrons”, which surrounds the atoms and does not belong to any of them in particular. For scientists, the presence of this cloud explains the good conductivity that metals have in relation to electricity, malleability and ductility.
Images: google images
Made by: Matheus Estevão, Pedro Julio, Pedro Miguel, João Baggio, João Guasque, Henrique Ozorio e Henrique Yasuda.