Células
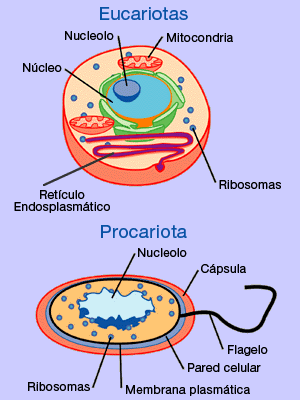
As Células são as unidades básicas de forma e função (morfofisiológicas) dos seres vivos. São divididas em procariontes e eucariontes.
Procariontes são as que o material genético não é protegido por membrana, ou seja, é solto no citoplasma.
Eucariontes são as que o material genético é protegido por membrana.
Partes das células e suas funções:
Ribossomos: são formados por subunidades, são formadas no núcleo de maneira independente, são responsáveis pela síntese de proteínas das células.
Lisossomos: são vesículas estéticas presentes apenas em células animais, possuem enzimas digestivas encarregadas de fazer a digestão celular
Retículo endoplasmático: conjunto de canalículos ramificados que transporta substâncias pelo citoplasma. É dividido em dois tipos:
Retículo endoplasmático liso : não possui ribossomos aderidos a sua superfície, e sua principal função é a síntese de lipídeos.
Retículo endoplasmático rugoso: possui ribossomos aderidos a sua superfície, e sua principal função é sintetizar as proteínas;
Complexo golgiense: sistema de bolsas achatadas chamadas de dictiossomos, interligados e sobrepostos, suas principais funções são armazenar as substâncias,fazer a secreção das substâncias armazenadas, síntese de glicídios e forma os lisossomos;
Mitocôndrias: São estruturas complexas e membranosas que fazem a respiração celular e geram ATP da célula;
Centríolos: estruturas tubulares formadas por microtúbulos que auxiliam no processo de divisão celular e formam estruturas como cílios e flagelos;
BIOLOGY
Cells
Cells are the basic units of form and function (morphophysiological) of living beings.
are divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes are those in which the genetic material is not membrane-protected, that is, it is released into the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes are those whose genetic material is membrane-protected.
Cell parts and their functions:
Ribosomes: they are formed by subunits, they are formed independently in the nucleus, they are responsible for cell protein synthesis.
Lysosomes: they are aesthetic vesicles present only in animal cells, they have digestive enzymes in charge of cell digestion
Endoplasmic reticulum: set of branched canaliculi that transport substances through the cytoplasm. It is divided into two types:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: it does not have ribosomes attached to its surface, and its main function is lipid synthesis.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum: it has ribosomes adhered to its surface, and its main function is to synthesize proteins;
Golgiense complex: system of flat bags called dictyosomes, interconnected and superimposed, its main functions are to store substances, secrete stored substances, synthesize carbohydrates and form lysosomes;
Mitochondria: These are complex, membranous structures that make cell respiration and generate cell ATP;
Centrioles: tubular structures formed by microtubules that help in the process of cell division and form structures such as cilia and flagella
Marco, Arthur Fernandes, Arthur Salata, Nicolas Antoni, Pedro Antunes.
Fonte da imagem da capa:
https://br.pinterest.com/pin/112308584457769153/

